Fever & Tropical illnesses
Tuberculosis (TB) / MDR-TB / XDR-TB
Chikungunya, Scrub Typhus

Urinary Tract Infections
Pneumonia / Pharyngitis / Tonsillitis
Influenza
COVID-19

Leprosy
Hepatitis (A to E)

HIV / AIDS
General Medicine & Infectious Disease
Fever & Tropical Illnesses
Fever is a common symptom of tropical illnesses, often caused by infections like malaria, dengue, or typhoid. These diseases, prevalent in warm climates, spread through vectors like mosquitoes or contaminated food and water. Symptoms include high fever, fatigue, and body aches. Early diagnosis using blood tests and prompt treatment with antimicrobials or antivirals are crucial. Preventive measures like vaccinations, hygiene, and vector control reduce risks significantly.


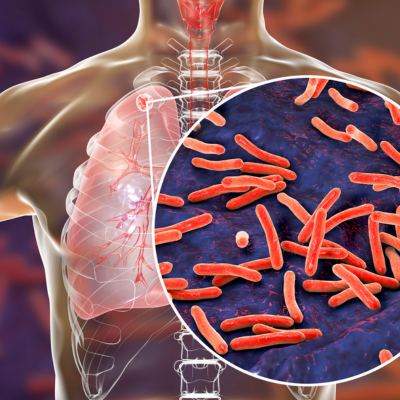
Tuberculosis (TB) / MDR-TB / XDR-TB
Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs. Symptoms include persistent cough, weight loss, and night sweats. Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) resists standard drugs, while extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) is harder to treat. Diagnosis involves sputum tests and imaging. Treatment requires prolonged antibiotic regimens. Early detection, adherence to therapy, and infection control measures are vital to manage and prevent the spread of TB.

Dengue, Typhoid, Malaria
Dengue, typhoid, and malaria are tropical diseases causing significant morbidity. Dengue, a viral infection, spreads via mosquitoes, presenting fever and joint pain. Typhoid, caused by Salmonella typhi, results from contaminated food, leading to fever and abdominal pain. Malaria, caused by *Plasmodium* parasites, causes cyclic fevers. Diagnosis relies on blood tests. Treatments include antimalarials, antibiotics, and supportive care. Prevention emphasizes mosquito control, hygiene, and vaccinations where available.

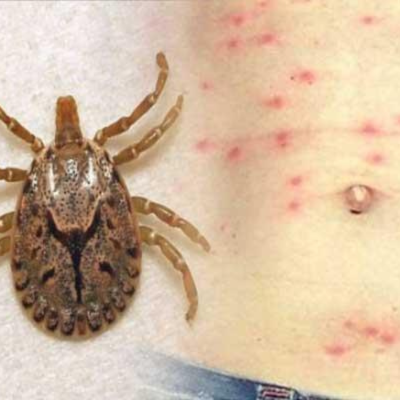
Chikungunya, Scrub Typhus
Chikungunya, a viral illness spread by mosquitoes, causes fever, severe joint pain, and rash, often resolving within weeks. Scrub typhus, caused by Orientia tsutsugamushi from mite bites, presents with fever, rash, and eschar at the bite site. Diagnosis involves serology or PCR. Treatment includes antivirals for chikungunya and antibiotics like doxycycline for scrub typhus. Prevention focuses on vector control and protective clothing in endemic areas.

Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are bacterial infections affecting the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. Common in women, symptoms include burning during urination, frequent urges, and pelvic pain. Escherichia coli is a frequent cause. Diagnosis uses urine culture. Antibiotics like nitrofurantoin are standard treatments. Severe cases may require hospitalization. Prevention includes hydration, hygiene, and avoiding irritants. Untreated UTIs can lead to kidney infections or sepsis if neglected.


Pneumonia / Pharyngitis / Tonsillitis
Pneumonia, an infection of the lungs, causes cough, fever, and breathing difficulty, often due to bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae. Pharyngitis and tonsillitis, commonly caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, lead to sore throat and fever. Diagnosis involves imaging for pneumonia and throat swabs for pharyngitis/tonsillitis. Antibiotics treat bacterial causes; supportive care helps viral cases. Vaccination and hygiene prevent spread. Severe cases may require hospitalization for oxygen or IV antibiotics.

Influenza
Influenza, a viral respiratory illness, causes fever, cough, sore throat, and muscle aches. Spread through droplets, it peaks seasonally. Complications like pneumonia are risks for the elderly or immunocompromised. Diagnosis uses rapid antigen tests or PCR. Antivirals like oseltamivir reduce severity if started early. Annual vaccination is the primary prevention method. Good hygiene, like handwashing and masking, reduces transmission. Most recover within a week with rest and hydration.


COVID-19
COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, spreads via respiratory droplets, causing fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Severe cases lead to pneumonia or organ failure. Diagnosis uses RT-PCR or antigen tests. Treatments include antivirals, steroids, and oxygen therapy for severe cases. Vaccination significantly reduces severity and spread. Preventive measures include masking, social distancing, and ventilation. Long COVID may cause persistent symptoms, requiring ongoing medical support and rehabilitation.

Leprosy
Leprosy, caused by Mycobacterium leprae, affects skin, nerves, and mucous membranes, leading to skin lesions and numbness. Spread through prolonged contact, it’s now rare due to effective treatments. Diagnosis involves skin biopsy and clinical evaluation. Multidrug therapy, including dapsone and rifampicin, cures most cases. Early treatment prevents disability. Stigma reduction and contact tracing are crucial. Preventive measures include early detection and treating infected individuals to halt transmission.


Hepatitis (A to E)
Hepatitis A to E are viral infections affecting the liver, causing jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal pain. Hepatitis A and E spread via contaminated food/water; B, C, and D transmit through blood or bodily fluids. Diagnosis uses blood tests for viral markers. Treatments range from supportive care (A, E) to antivirals (B, C). Vaccination prevents A and B. Safe practices, like sterile needles and hygiene, reduce transmission risks.

HIV / AIDS
HIV weakens the immune system by attacking CD4 cells, leading to AIDS if untreated. Transmitted through blood, sexual contact, or mother-to-child, symptoms include fever and fatigue. Diagnosis uses antibody or PCR tests. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) suppresses the virus, enabling near-normal lifespans. Prevention includes condoms, PrEP, and safe needle practices. Regular testing and early treatment are critical. Stigma reduction and education support effective management and prevention.


Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis spread through sexual contact. Symptoms vary, including discharge, sores, or none (asymptomatic). Diagnosis involves swabs, blood tests, or urine analysis. Antibiotics treat bacterial STDs; antivirals manage herpes or HPV. Condoms and regular screening reduce transmission. Untreated STDs can cause infertility or cancer (e.g., HPV). Education, vaccination (HPV), and partner notification are key for prevention and control.

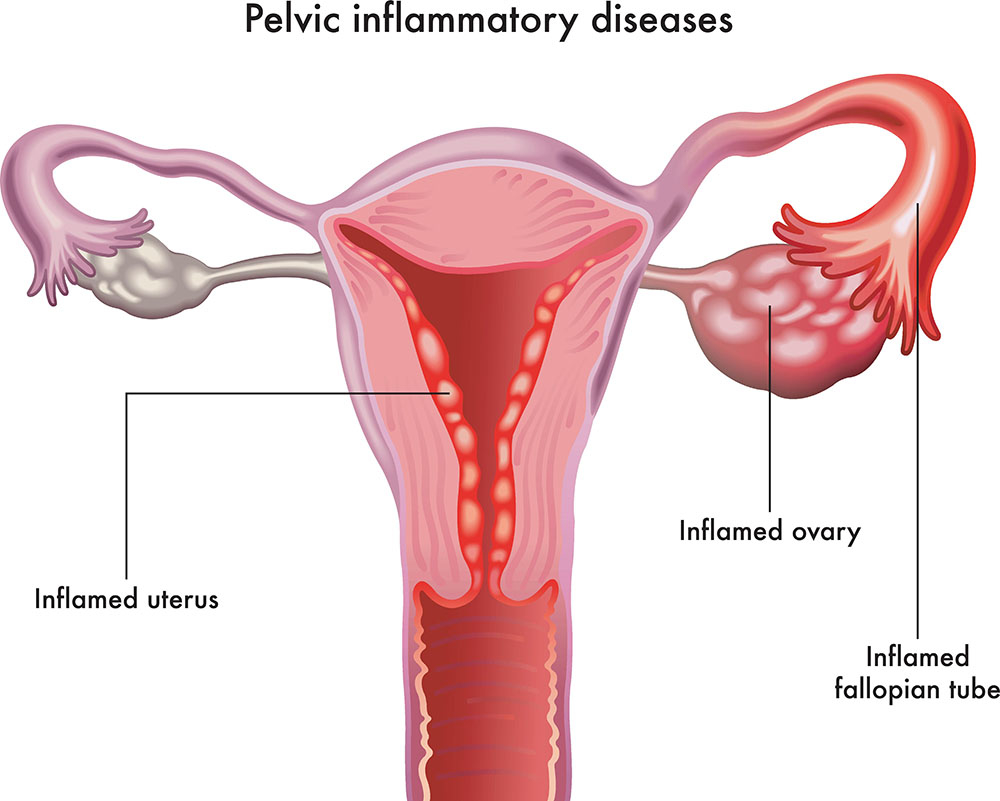
Endometritis / Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Endometritis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) are infections of the uterine lining or reproductive organs, often caused by bacteria like Chlamydia or Gonococcus. Symptoms include pelvic pain, fever, and abnormal discharge. Diagnosis uses clinical evaluation, imaging, or laparoscopy. Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment. Untreated cases risk infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Prevention includes safe sex practices and early STD treatment. Regular gynecological care aids early detection.
Giardiasis / Filariasis
Giardiasis, caused by Giardia lamblia, spreads via contaminated water, causing diarrhea and abdominal pain. Filariasis, from parasitic worms, spreads through mosquito bites, leading to lymphedema or elephantiasis. Diagnosis uses stool tests for giardiasis and blood smears for filariasis. Treatments include metronidazole for giardiasis and antiparasitics like diethylcarbamazine for filariasis. Prevention involves clean water, sanitation, and mosquito control. Early treatment prevents chronic complications like lymphatic damage.

Amoebiasis
Amoebiasis, caused by Entamoeba histolytica, spreads through contaminated food or water, causing diarrhea, abdominal pain, or liver abscesses. Asymptomatic carriers can spread the parasite. Diagnosis uses stool tests or imaging for abscesses. Metronidazole is the primary treatment, followed by paromomycin to clear cysts. Prevention includes safe drinking water, hygiene, and proper sanitation. Untreated cases may lead to severe complications like liver abscess or intestinal perforation.
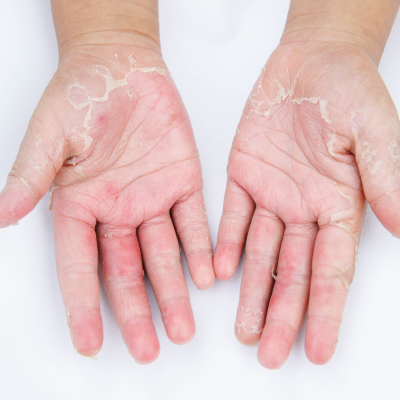
Invasive Fungal Infections (Candidiasis, Aspergillosis, Mucormycosis)
Invasive fungal infections like candidiasis, aspergillosis, and mucormycosis affect immunocompromised individuals. Candidiasis causes systemic infections; aspergillosis impacts lungs; mucormycosis affects sinuses or tissues. Symptoms include fever, organ dysfunction, or tissue necrosis. Diagnosis uses cultures, imaging, or biopsies. Antifungals like amphotericin B or voriconazole are treatments. Prevention involves managing underlying conditions (e.g., diabetes) and reducing fungal exposure. Early intervention is critical to improve outcomes.

Dermatophytosis
Dermatophytosis, or ringworm, is a fungal infection of skin, hair, or nails caused by Trichophyton or Microsporum. It presents as itchy, circular rashes. Spread occurs through direct contact or contaminated surfaces. Diagnosis involves skin scrapings or fungal culture. Topical antifungals like clotrimazole treat mild cases; oral antifungals manage severe infections. Prevention includes hygiene, avoiding shared items, and keeping skin dry. Prompt treatment prevents spread and complications.
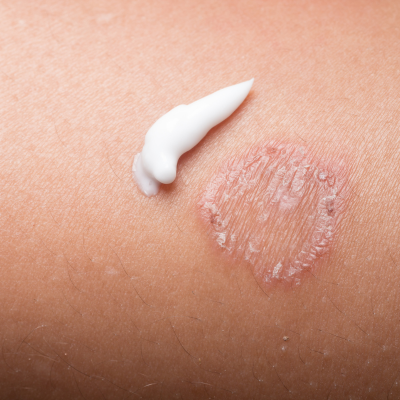
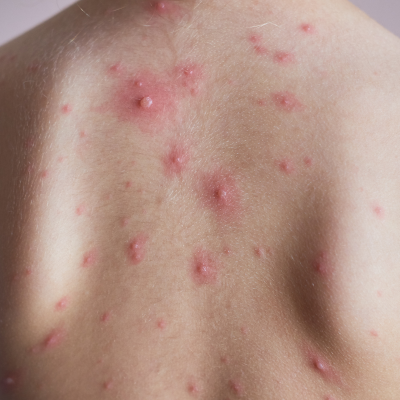
Herpes Infections / Chickenpox
Herpes infections, including HSV-1/2 and varicella-zoster (chickenpox), cause painful sores or rashes. Chickenpox spreads via respiratory droplets, leading to itchy blisters; herpes spreads through contact. Diagnosis is clinical or via PCR. Antivirals like acyclovir reduce severity. Vaccination prevents chickenpox and shingles (zoster). Good hygiene and avoiding contact with lesions limit spread. Complications like shingles or encephalitis require prompt treatment in immunocompromised patients.

Meningitis / Encephalitis
Meningitis and encephalitis are infections of the brain or its membranes, caused by bacteria (e.g., *Neisseria meningitidis*), viruses, or fungi. Symptoms include fever, headache, neck stiffness, or confusion. Diagnosis uses lumbar puncture, imaging, or PCR. Bacterial meningitis requires urgent antibiotics; viral cases often need supportive care. Vaccination (meningococcal, pneumococcal) and hygiene prevent spread. Early treatment is critical to avoid neurological damage or death.